Anatomy of Leaf
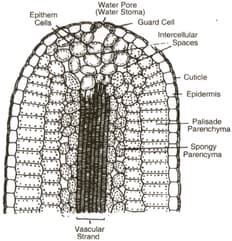
Anatomy of Leaf: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Subsidiary Cells, Leaf Epidermis, Kranz Anatomy, Epiblema, Sunken Stomata, Guttation, Hydathode, Epidermal Tissue System, Cuticle, Trichomes, Stomatal Apparatus, Dicot Leaf, and Monocot Leaf.
Important Questions on Anatomy of Leaf
Give examples of plants with sunken stomata.
What are the functions of subsidiary cells?
Guttation happens due to the development of
Identify the incorrect statement of Bulliform cells _____.
The structures involved in the process of guttation are:
Which one of the following anatomical structures is involved in guttation?
Which of the following characters is not a difference between dicot and monocot leaves?
Epidermal hairs of shoot system
(I) Unicellular or Multicellular
(II) Multicellular, branched or unbranched
(III) Secretary in function
(IV) Absorbs water
(V) Prevent transpiratory water loss
During guttation, the oozed liquid contains:
In the vascular bundles of dorsoventral and isobilateral leaves, protoxylem and phloem respectively situated towards:
Guttation differs from transpiration in which aspect?
The process responsible for facilitating loss of water in liquid form from the tip of grass blades at night and in early morning is
Which of the process is responsible for loss of sugars and salts from plants